From the outset, I'll admit that I'm a regular Starbucks customer, frequenting locations in Boston, multiple U.S. cities, and internationally. Whether I'm in Paris or Tokyo, I visit Starbucks for a taste of home and because I enjoy my cappuccinos prepared dry while also being curious about the consistency across locations. I believe there is much to learn from successful companies like Starbucks. However, this is a mini-case study designed to help startups understand the key factors that contribute to scaling.
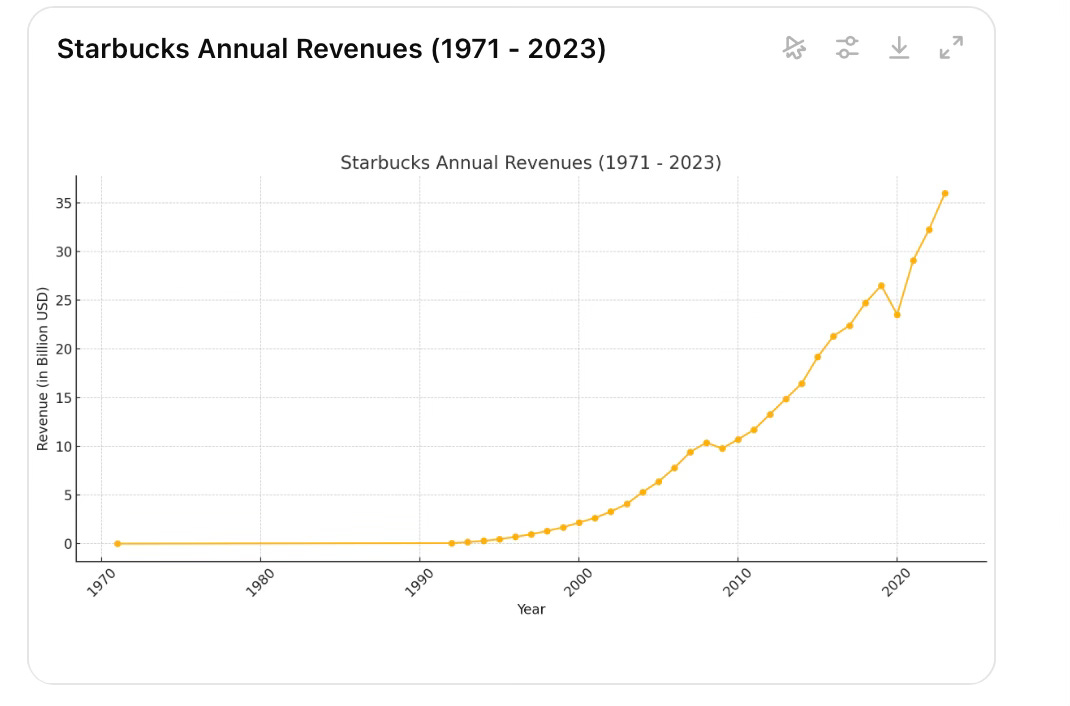
From its inception in 1971 to 2023, Starbucks' annual revenues (see chart below) have grown significantly, achieving a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 27.89%. This reflects the company's impressive growth over more than five decades.
Throughout its history, Starbucks has faced periods of sales decline due to several factors. During the 2008 financial crisis, consumer spending decreased significantly, challenging Starbucks as a premium brand. The company responded by closing underperforming stores and restructuring. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 led to temporary store closures and a shift toward at-home coffee consumption, reducing foot traffic and sales while causing supply chain disruptions. Increased competition from other coffee chains like Dunkin' and McDonald's, shifts in consumer preferences toward healthier and more sustainable options, and operational challenges such as store renovations and labor strikes have also impacted sales. Despite these challenges, Starbucks has consistently adapted its strategy, expanded its product offerings, and enhanced its digital and delivery capabilities to mitigate declines and drive long-term growth.
Starbucks' ability to scale its revenues since 1971 can be attributed to group of key strategies and initiatives:
Rapid Expansion: Starbucks entered diverse geographic locations and established multiple locations in key cities.
Brand Recognition and Loyalty: The company built a strong brand and cultivated a loyal customer base.
Product Diversification: Starbucks expanded its menu beyond coffee to include a variety of beverages and food items.
Embracing Technology: The company invested in technology such as mobile apps, mobile ordering, and payment systems to enhance customer experience.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions: Starbucks acquired companies like the Seattle Coffee Company and Teavana and partnered with food and beverage brands to diversify its offerings.
Sustainability Initiatives: Starbucks appealed to environmentally conscious consumers by emphasizing sustainability and ethical sourcing.
Global Adaptation: The company adapted its stores and menu offerings to fit local cultures and preferences in international markets.
Focus on Customer Experience: Starbucks created a welcoming environment where customers can relax or work.
Innovation in Product Development: The company consistently introduced new products and limited-time offerings to keep its menu fresh and relevant.
Investment in Employee Training and Culture: Starbucks emphasized customer service excellence by investing in employee training and fostering a positive company culture.
Startups can enhance customer experience, develop new products, build brand equity, diversify their offerings, and establish partnerships even in the early stages. As they grow into emerging companies and eventually reach later stages, these factors become more critical and attainable.
Startups can learn from Starbucks’ success in balancing rapid expansion with maintaining quality and consistency, leveraging technology to personalize customer interactions, and continuing to innovate in product offerings while staying true to its core brand. For startups and Starbucks alike, strengthening customer loyalty, solidifying its brand and fostering a positive work environment are ways to ensure high levels of customer service and satisfaction, driving long-term growth.