NVIDIA Today & Rise to Power
In 2023 and 2024, Wall Street struggled to predict NVIDIA's stock performance. This year the company’s shares surged 64%, adding over $700 billion in market value since January. Last week's earnings release robustly topped estimates with a 265% revenue jump, catalyzing a historic $277 billion single-day stock surge on Thursday.
Building on Nvidia's earnings call, two significant highlights emerged: The impending launch of the revolutionary Blackwell GPUs with exceptional performance, and Nvidia's evolving business landscape, now predominantly focused on AI inference (70%) over training (30%), signaling the increasing accessibility of AI technologies to end-users and their integration into everyday applications.
NVIDIA's startup journey serves as a valuable lesson. Established in 1993 by Jensen Huang (now CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem, the company initially centered its efforts on gaming GPUs. Despite facing compatibility issues in 1995 and 1996, their pivotal breakthrough with the RIVA 128 GPU in 1997 catapulted NVIDIA into a prominent position in the graphics market. Expanding into gaming, professional visualization, and high-performance computing throughout the late 1990s and early 2000s, NVIDIA later pioneered GPU applications in scientific computing and artificial intelligence (AI). Strategic partnerships and continuous innovation cemented their position as a global leader.
In retrospect, NVIDIA's success is rooted in several key strengths:
Early focus on GPUs: Pioneering their capabilities with various tasks, including AI and scientific computing.
Strong Developer Ecosystem: Extensive support empowers enterprise data centers or via the Cloud and GenAI vendors.
Product Diversification and Innovation: Expanding beyond gaming and adapting to computing trends in the enterprise data center and cloud services arena.
Market Leadership: Strong position in key areas, particularly AI.
"Grace is the silent voice that speaks loudest in the heart."
Undoubtedly, innovation in chip technology has fueled NVIDIA's rise. To understand their capabilities, consider their new Grace Hopper Superchip:
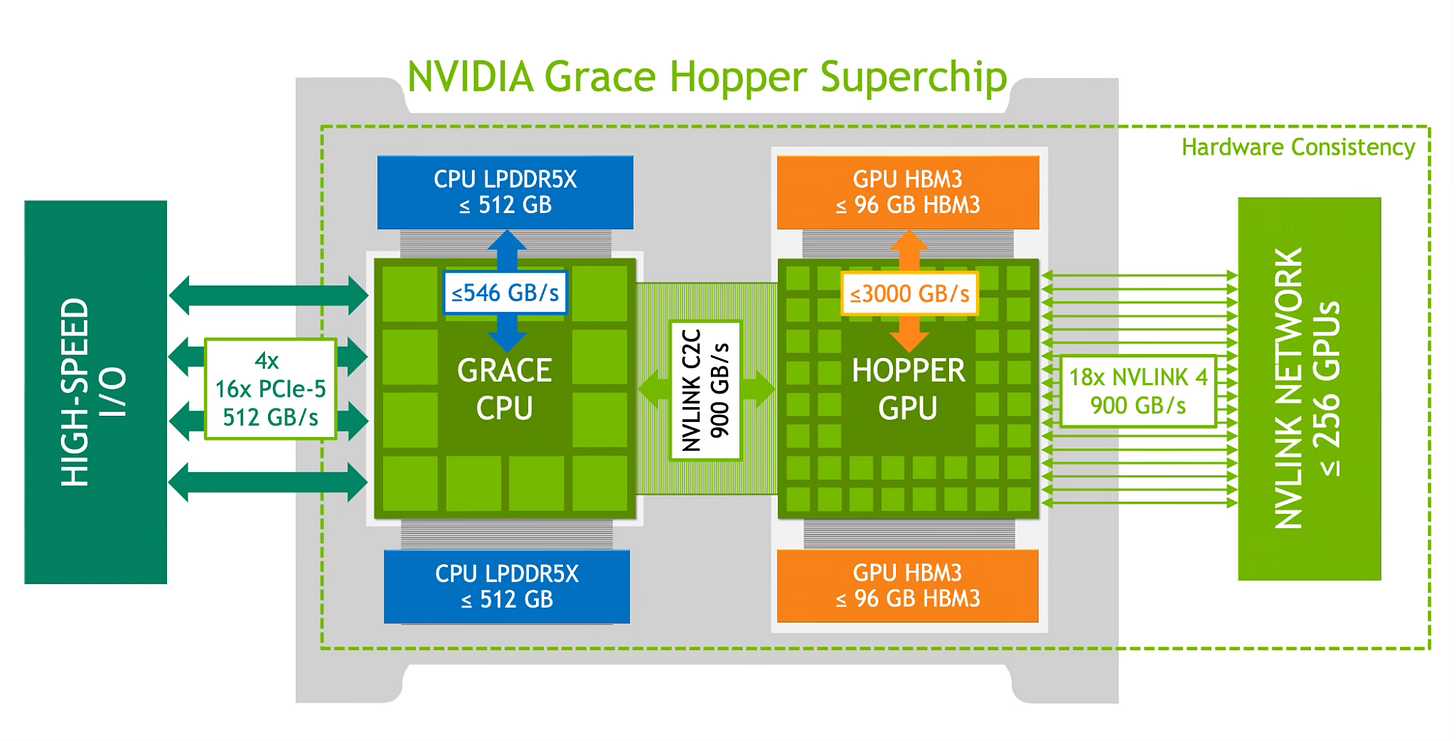
NVIDIA's "Grace Hopper Superchip" represents a radical departure from traditional processors, optimized for AI workloads. At its heart, Grace has a highly advanced CPU or main processor that offers significant efficiency and speed improvements compared to Intel chips.
Grace’s dedicated AI architecture delivers 10x higher processing speed for deep learning while saving energy. Tight integration between Grace’s CPU and GPU cores, seamless integration, and unified programming models simplify development.
Combined with Hopper GPU, it showcases NVIDIA's vision for revolutionizing AI by pairing a specialized processor designed to handle graphics processing tasks with one that focuses on computationally intensive tasks. Hopper offers an order of magnitude more compute power and memory bandwidth compared to its predecessors.
Together, the Grace CPU and Hopper GPU architectural breakthroughs showcase NVIDIA's technical vision and silicon expertise aimed at revolutionizing artificial intelligence. Just as Intel powered the PC revolution, NVIDIA's Grace Hopper Superchip promises to unlock the next era of AI innovation in the cloud, data center, and corporate computing across industries.
While powerful, the Grace Hopper Superchip is one piece of a larger picture contributing to NVIDIA's success.
Major chipmakers like Intel, Broadcom, and Qualcomm provide customer and developer support, but with variations. Major chipmakers offer varied support options. All three companies offer multi-tiered support systems and developer resources like SDKs and forums.
NVIDIA provides extensive support through its Developer Program, including free access to hundreds of software and performance analysis tools. This includes SDKs, pre-trained models, containerized applications, and source code across various fields like AI, HPC, robotics, and more. Users have access to free tools, resources, training, and community support. This also has tons of technical documentation, but they have peer and domain expert help. Developers can connect with a global community of peers and NVIDIA experts through forums, Q&A platforms, and social media channels. Also, they have information on the right hardware: NVIDIA provides guidance on selecting the appropriate hardware (e.g., GPUs) for tackling specific development challenges. They additional support, like Intel and Broadcom, in the form of training and events.
While competition is rising, NVIDIA's software advantage creates "vendor lock-in. NVDA’s software advantage starts with Compute Unified Architecture (CUDA), a platform for general-purpose processing on Nvidia’s GPUs. CUDA is not an operating system, but it has come to serve as the software layer for AI innovation. While NVDA is described as a chip company still, it is clear that CEO Jensen Huang understood long-term competitive advantage was going to come from software.
In 2017, CEO Huang told MIT Tech Review, “Software is eating the world, but AI is going to eat software.”
Fast forward to 2024, and here is Huang on stage recently at the World Government Summit in Dubai, explaining exactly how this is happening. He said the well-worn advice that young people should learn to code is wrong.
“In fact, it’s almost exactly the opposite. It is our job to create computing technology such that nobody has to program. And that the programming language is human. Everybody in the world is now a programmer. This is the miracle of artificial intelligence.”
NVIDIA’s customers buy its A100 and H100 chips to train and run AI models, but do that work via NVIDIA’s proprietary software. Customers rely on NVIDIA's software for AI models, making it difficult to switch providers. And reorder again. Hence, the sustained dominance.
In summary, NVIDIA's unique combination of technology, strategy, ecosystem, and operations drives sustained growth. This multi-dimensional edge positions the company for long-term success.